Risk Management
Accountability
Risk management is a collective responsibility shared across various stakeholders in Sasol, rather than solely resting on the shoulders of a dedicated risk team. The different stakeholders contribute to effective risk management through their roles.
The Businesses and operational teams are responsible for identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks specific to their areas of operation. They have firsthand knowledge of the risks associated with their activities and processes and play a crucial role in implementing risk controls and monitoring risk exposure. Risk management does not reside solely with the risk teams.
Sasol has a centralised risk management function in the Corporate Centre which is structurally independent of the Businesses and other Corporate Centre functions. This team is responsible for enabling enterprise risk management across the organisation, aligned with changes in our operating model and approved delegation of authority levels. The team is led by the Chief Risk Officer (CRO) who reports to the EVP: Strategy, Sustainability and Integrated Services (SSIS) who has executive accountability for Sasol’s global risk management process and in turn reports to the CEO. The centralised team has a unique role to play in supporting the process of defining risk appetite and ensuring that risk management is integrated into strategic risk decision-making. This team plays a vital supporting role by providing expertise, tools, and methodologies to help identify, assess, prioritise, and mitigate risks across the organisation with a focus on facilitating risk awareness and providing guidance on risk management principles and practices. This team is also required to champion a strong risk-aware culture where employees understand their role in identifying and reporting risks.
Every individual within the organisation has a role to play in risk management. Employees are often the first line of defence against operational risks and are responsible for adhering to policies, procedures, and controls established to mitigate risks. External stakeholders, including customers, suppliers, regulators, and investors can also influence our risk profile. Understanding and managing the expectations and concerns of these stakeholders is a key part of our risk management process.
Risk Governance and Oversight
To ensure decisions align with our strategy and execution, we adhere to an integrated governance and oversight process in managing our uncertainties. These facilitate the coordination and management of risks throughout our organisation, with dedicated oversight provided by the Board of Directors (Board), Board Committees, and Group Executive Committee, all operating within their defined terms of reference.
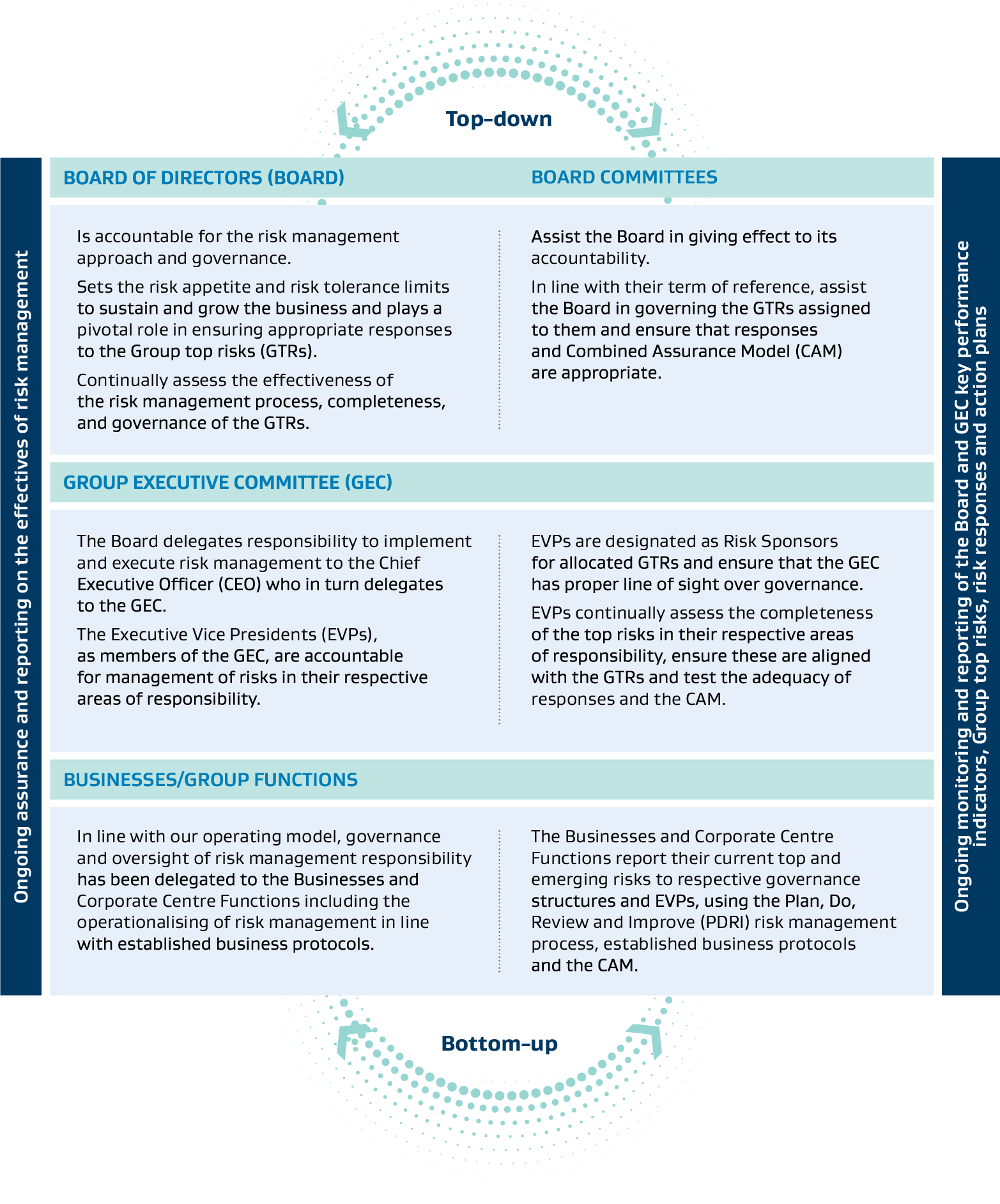
Sasol has a dedicated governance structure to review and oversee its risk management process and Group top risks (GTR). Our Group's top risks are categorised within applicable risk themes. These, together with the associated risks and related developments, are reported in line with the approved governance process.
Governance Principles
GTR themes are allocated to the GEC as our Executive Vice President (EVP) sponsors and to the Board and its Sub-committees in alignment with their accountabilities, mandates, and Committee Terms of References. The EVPs are accountable for risks in their areas of responsibility, and they are supported lower down the organisation by senior leaders and their respective teams to ensure that effective key responses and critical controls are in place to mitigate the risk exposure to acceptable levels.
The table below provides an overview of the relevant aspects (key business imperatives), GTRs, relevant EVP sponsors, allocated GEC Committees, and accountable Board and Board Sub-committees.
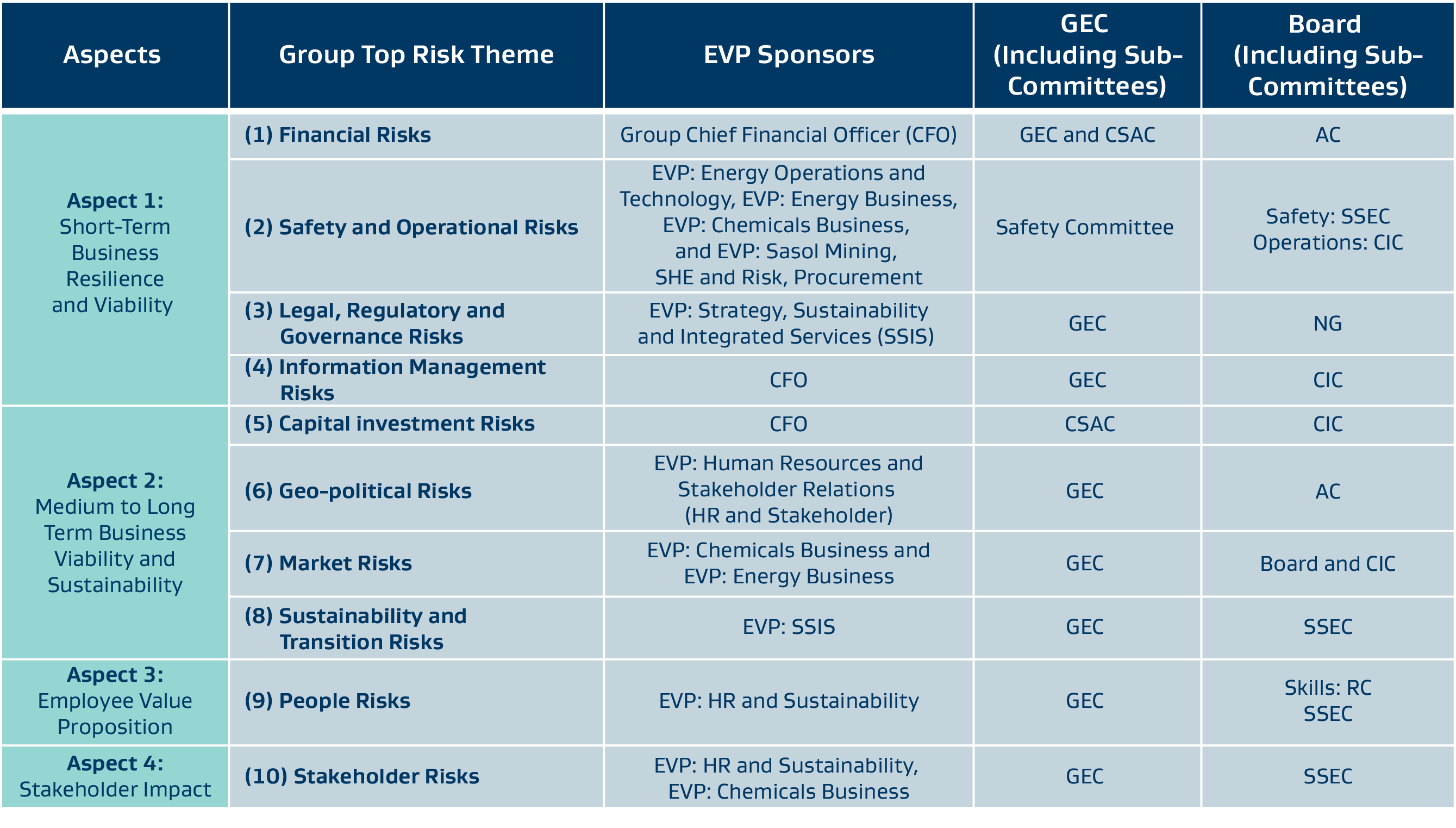
Committees Legends: GEC = Group Executive Committee; CSAC = Capital Structure Allocation Committee; SSEC = Safety; Social & Ethics Committee; AC = Audit Committee; RC = Remuneration Committee; CIC = Capital Investment Committee; NG = Nomination & Governance Committee
Enterprise Risk Management Processes
The ERM process is enabled through our risk management fundamentals which direct all risk management behaviours, actions and decisions and are implemented in accordance with our values. Integrated into day-to-day decision-making, these fundamentals provide the foundation of effective risk management.
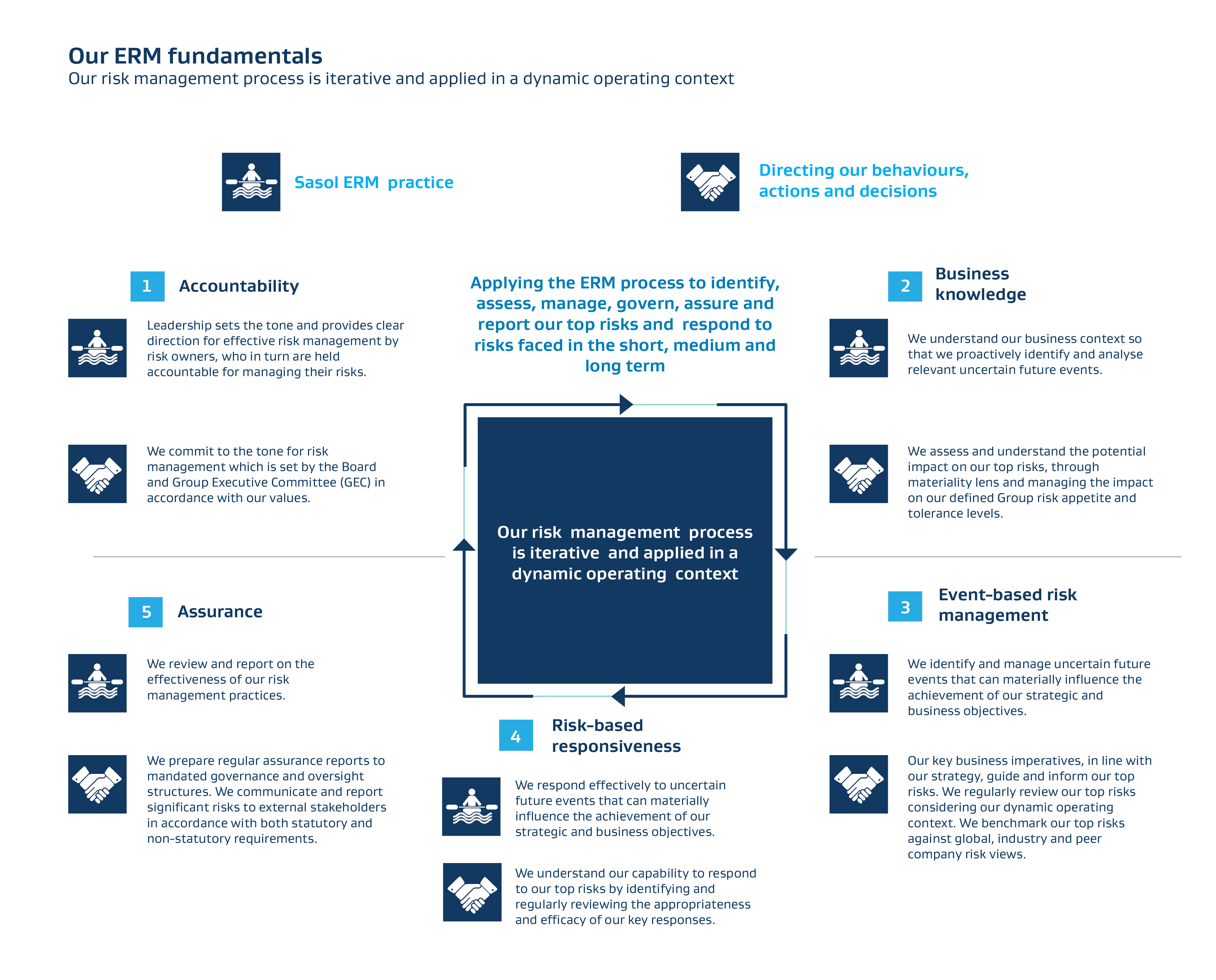
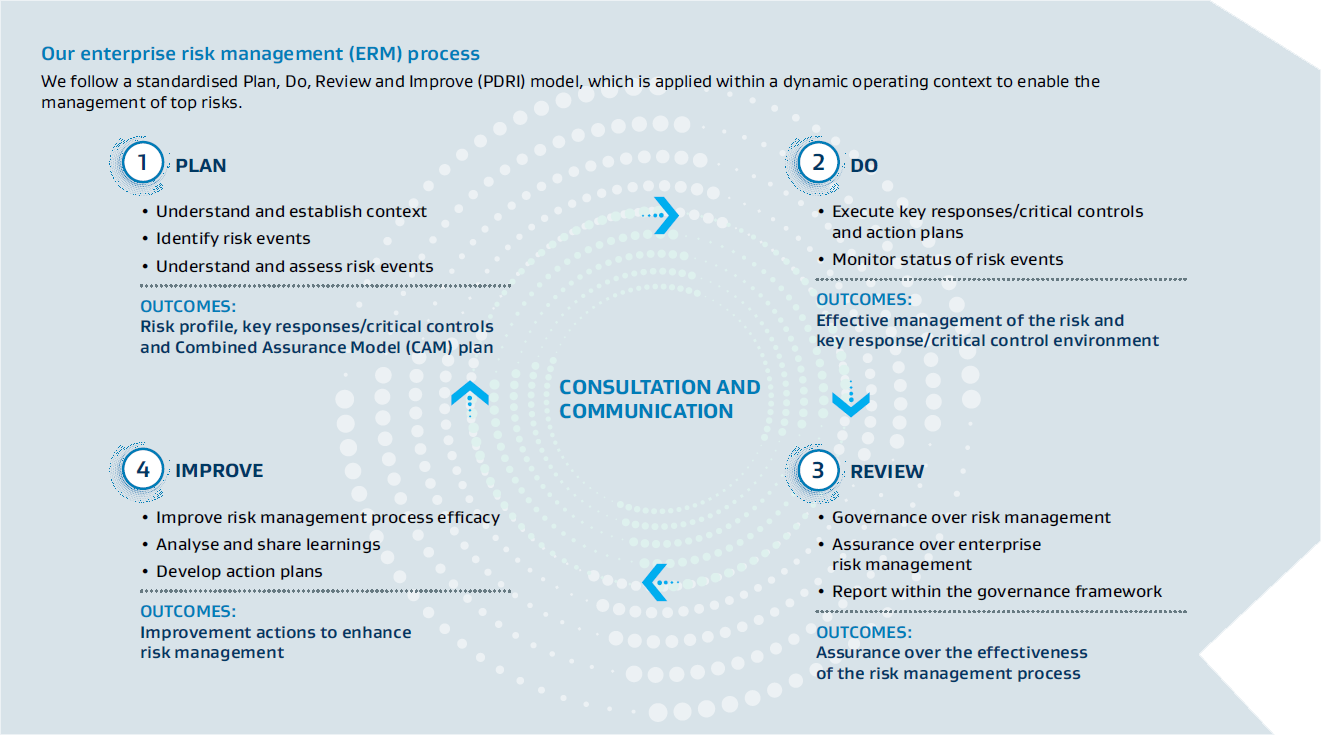
Our ERM process directs our approach to identify, understand, and respond to significant risks associated with our business. In executing our ERM process, we follow a Plan, Do, Review and Improve (PDRI) model where we identify, understand, execute, monitor, govern, assure, and report on our top risks and respond to significant risks being faced in the short, medium and long term. Our approach to risk management is intricately connected to our strategy, strategic objectives, material matters, and Group top priorities. Sasol’s risk management process is aligned with external frameworks like King IV, COSO, and ISO 31000.
As part of our GTRs review and monitoring process, we report risk-related matters on a quarterly basis to our GEC and Board. This includes reporting on key developments in the internal and external environment associated with our GTRs and watchlist risks (including emerging risks). The reporting aligns with our governance framework as shown above.
Our approach to integrated risk management is targeted towards an effective process that directs our behaviours and activities. In achieving integration, we aim to deliver on the following:
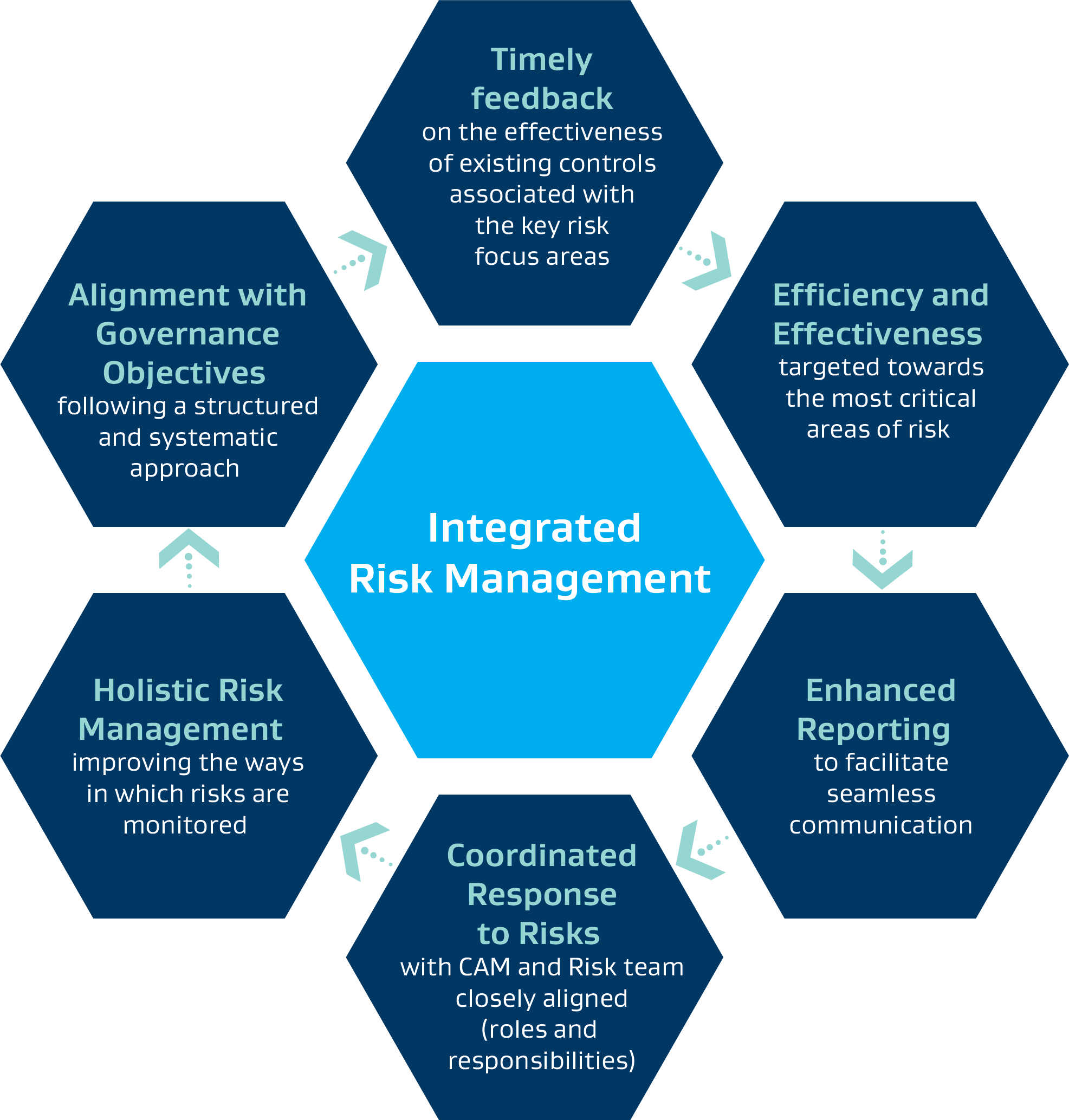
Effectiveness of the Risk Management Process
The annual review of the risk management process by the internal audit team, Sasol Assurance Services (SAS), underscores the importance of independent assessment and oversight in ensuring the effectiveness of risk management practices within the organisation. Such reviews are prioritised and approved by the Audit Committee. As part of their mandate, the internal audit team, led by the Chief Assurance Officer, conducts audits to evaluate the adequacy and effectiveness of various processes and controls across the organisation. In this case, they focus specifically on auditing the risk management function and process. The review encompasses a comprehensive evaluation of the risk management framework, methodologies, policies, and procedures in place within the organisation. This includes assessing how risks are identified, assessed, prioritised, and mitigated across different business units and functions.
SAS operates independently from the risk management function to ensure unbiased assessments. Their findings and recommendations are based on objective analysis, aiming to provide an accurate assessment of the strengths and weaknesses of the risk management process. The Chief Assurance Officer has a direct reporting line to the Audit Committee, which is a sub-group of the board of directors responsible for overseeing the organisation's internal control processes, including risk management. This reporting structure ensures transparency and accountability at the highest level of governance. The Audit Committee prioritises and approves the annual review of the risk management process, highlighting its significance in Sasol’s governance framework. This committee plays a critical role in providing oversight and guidance to ensure that risk management practices align with the organisation's strategic objectives and regulatory requirements. The insights and recommendations generated from the annual review serve as valuable input for enhancing our overall risk management capabilities. By identifying areas for improvement and implementing corrective actions, Sasol is able to strengthen its operational resilience and long-term viability.



